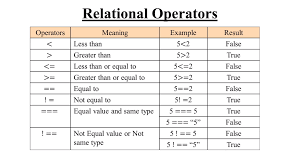
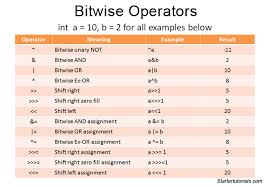
TYPE’S OF PILLAR’S ;
> INHERITANCE
> POLYMORPHISM
> ABSTRACTION
> ENCAPSULATION

> Now, that we will move a four pillars of the opps. Below the.
> Before see the , definition of class and objects .
CLASS ;
> class is a user-defined blueprint from which objects are created.
> It represents the set of properties or methods that are common to all objects of one type.
> Using classes, you can create multiple objects with the same behavior instead of writing their code multiple times.
> In general, class declarations can include these components in orde.
CLASS NAME ;
> The class name should be with the initial letter for capital by convention.
INTERFACE ;
> A comma-separated list of interfaces implemented by the class.
> if any, preceded by the keyword implements.
BODY ;
> the body tag is surrounded for the class braces. {}
OBJECT ;
> that represents real-life entities. A typical Java program creates many objects.
> which as you know, interact by invoking methods.
> The objects are what perform your code, they are the part of your code visible to the viewer. An object mainly user.
INDENTITY ;
> It is a unique name given to an object ,that enables it to interact with other objects.
INHERITANCE ;
> Inheritance is an important pillar of OOP’S.
> It is the mechanism in Java by which one class is allowed to inherit the features of another class.
> Exp ; A child inherits the traits of her parent.
> With inheritance, we can reuse the fields and methods of the existing class.
TYPES OF INHERITANCE ;
> SINGLE INHERITANCE
> MULTIPLE INHERITANCE
> MULTILEVEL INHERITANCE
> HIERARCHICAL INHERITANCE
> HYBRID INHERITANCE
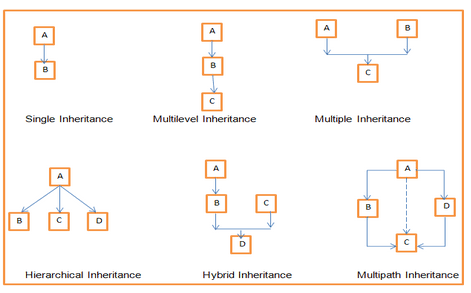
SINGLE INHERITANCE ;
> In Single Inheritance one class extends another class ,one class only.
> EXP ,Class B extends only Class A. Class A is a super class and Class B is a Sub-class.
MULTIPLE INHERITANCE ;
> Java does not support multiple inheritance.
> EXP, Class C extends Class A and Class B both.
MULTILEVEL INHERITANCE ;
> Multilevel Inheritance, one class can inherit from a derived class.
> Hence, the derived class becomes the base class for the new class.
>EXP, Class C is subclass of B and B is a of subclass Class A.
HIERARCHICAL INHERITANCE ;
> Hierarchical Inheritance, one class is inherited by many sub classes.
> Exp, Class B, C, and D inherit the same class A.
HYBRID INHERITANCE ;
> Hybrid inheritance is one of the inheritance types in Java which is a combination of Single and Multiple inheritance.
> exp , all the public and protected members of Class A are inherited into Class D, first via Class B and secondly via Class C.
PROGRAM EXAMPLE ;
class Doctor
{
Public static void Doctor_Details()
{
System.out.println(“Doctor Details…”);
}
}
class Surgeon extends Doctor
{
void Surgeon_Details() {
System.out.println(“Surgen Detail…”);
}
}
public class Hospital
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
Surgeon s = new Surgeon();
s.Doctor_Details();
s.Surgeon_Details();
}
}
POLYMORPHISM ;

> Polymorphism means *many forms*. And it occurs when we have many classes that are related to each other by inheritance.
> Inheritance lets us inherit attributes and methods from another class.
> Polymorphism uses those methods to perform different tasks.
> This allows us to perform a single action in different ways.
TYPES OF POLYMORPHISM ;
> COMPLIE TIME POLYMORPHISM
> RUN-TIME POLYMORPHISM
COMPILE TIME POLYMORPHISM ;
> It is also known as static polymorphism. This type of polymorphism is achieved by function overloading.
METHOD OVERLOADING ;
> When there are multiple functions with the same name but different parameters then these functions are said to be overloaded.
METHOD OVERRIDING ;
> It is also known as Dynamic Method Dispatch.
> It is a process in which a function call to the overridden method is resolved at Runtime.
> This type of polymorphism is achieved by Method Overriding.
PROGRAM ;
class Animal
{
public void animalSound()
{
System.out.println(“The animal makes a s ound”);
}
}
class Pig extends Animal
{
public void animalSound()
{
System.out.println(“The pig says: wee wee”);
}
}
class Dog extends Animal
{
public void animalSound()
{
System.out.println(“The dog says: bow wow”);
}
}
class Main
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Animal myAnimal = new Animal(); // Create a Animal object
Animal myPig = new Pig(); // Create a Pig object
Animal myDog = new Dog(); // Create a Dog object
myAnimal.animalSound();
myPig.animalSound();
myDog.animalSound();
}
}
> Another types will be soon …….