EXPLAIN ;

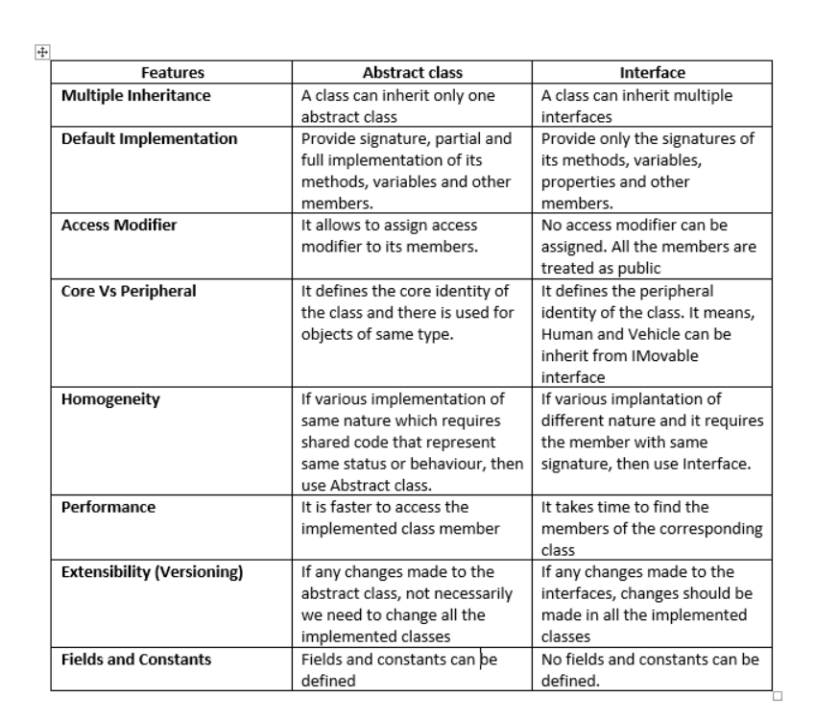
> An interface in Java is a blueprint of a class. A Java interface contains static constants and abstract methods.
> The interface in Java is a mechanism to achieve abstraction.
> A class implements an Interface to inherit the abstract methods.
ADVANTAGES ;
> Java Interface supports Multiple Inheritance.
> Java Interface enables programmers to break up the complex programming approaches.
> simplify the dependencies between the objects.
Java Interface makes the data members.
> methods in an application to be loosely coupled.
DISADVANTAGES ;
> Use of Java Interface brings down the execution speed of the application.
> Java Interfaces in the application are either used repeatedly at large extent or hardly used at all.
ABSTRACT ;

> Abstract class can have abstract and non-abstract methods.
> Abstract class doesn’t support multiple inheritance.
> Abstract class can have final, non-final, static and non-static variables.
> An abstract class can be extended using keyword extends.
PROGRAM ;

interface In1 {
// public, static and final
final int a = 100;
// public and abstract
void display();
}
class TestClass implements In1 {
public void display() {
System.out.println(“values”);
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
TestClass t = new TestClass();
t.display();
System.out.println(a);