EXPLAIN ;

> Abstraction ; the process of hiding certain details and showing only essential information to the user.
EXAMPLE ;
> it shows only essential things to the user and hides the internal details, for example, sending SMS where you type the text and send.
TYPES ;
> There are two type uses in abstraction.
> Data abstraction
> process abstraction
DATA ABSTRACTION ;
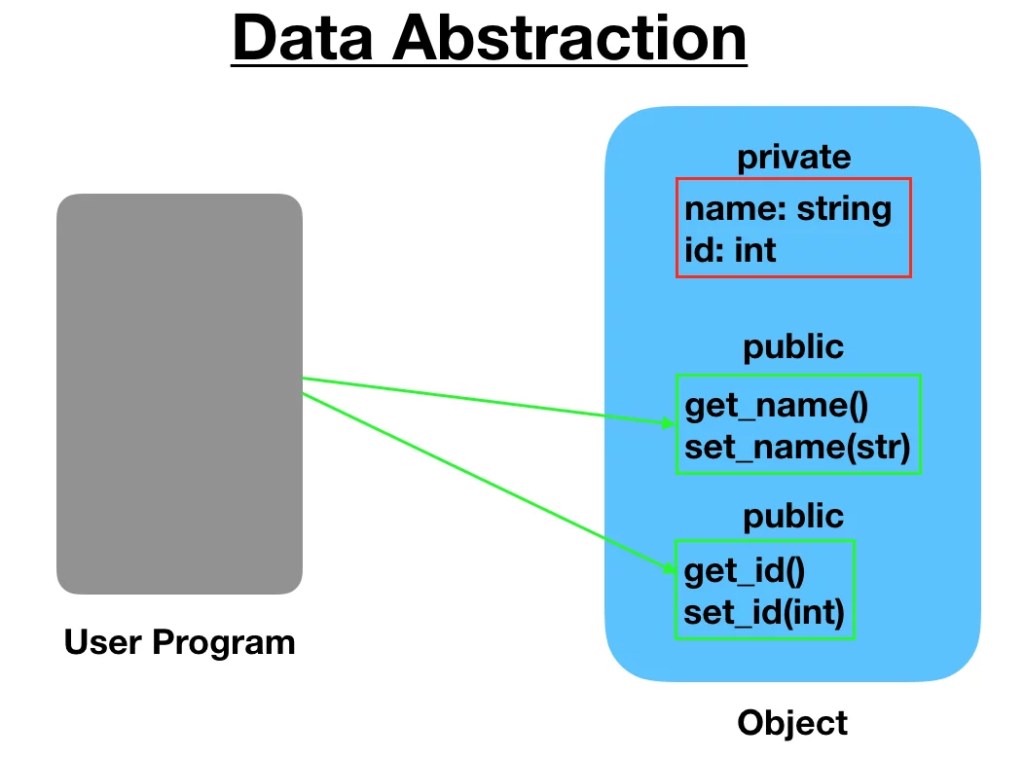
> When the object data is not visible to the outer world, it creates data abstraction.
> If needed, access to the Objects’ data is provided through some methods.
PROCESS ABSTRACTION ;
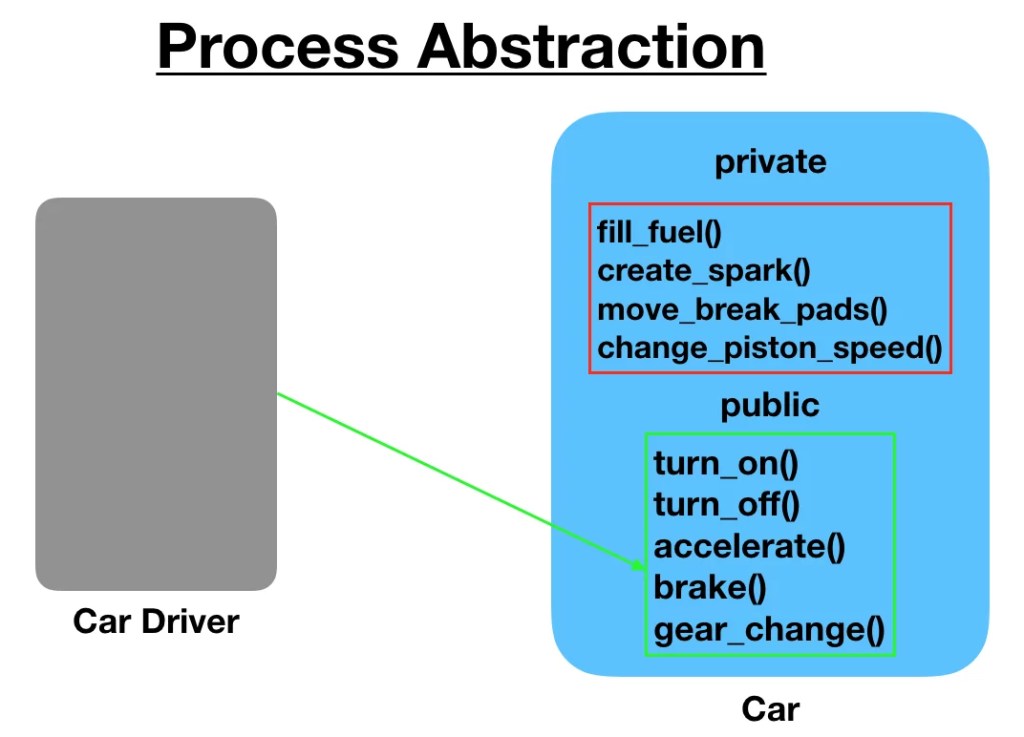
> We don’t need to provide details about all the functions of an object.
> When we hide the internal implementation of the different functions involved in a user operation, it creates process abstraction.
PROGRAM ;
abstract class Bank{
abstract int Interest();
}
class SBI extends Bank{
int Interest() {
return 100;
}
}
class IOB extends Bank. {
int Interest() {
return 50;
}
}
class TestBank. {
public static void main(String args[]) {
Bank b;
b=new SBI();
System.out.println (“the Interest is:”+Interest()+” %”);
b=new IOB();
System.out.println (“the. Interest is: “+b.Interest()+” %”);
}
}
USING A DOUBLE (FOR LOOP) ;
Public class line {
Public static void main(String[]args) {
Int num = 1 ;
For(int row = 5; row>=1; row–) {
For(int col = 1; col<=1; col++) {
System.out.print(row+” “+num);
}
System.out.println();
Num++;
}
}
}
USING A DOUBLE (WHILE LOOP) ;
Public class line2 {
Public static void main (String[]args) {
Int row = 1;
While ( row <=7) {
Int col = 1 ;
While ( col <=7) {
System.out.print(col);
Col++;
}
Row++;
System.out. println(” “);
}
}
}