
WHAT IS CONTROL STATEMENT ;
>control statement in java is a statement that determines whether the other statements will be executed or not.
>It controls the flow of a program.
> An ‘if’ statement in java determines the sequence of execution between a set of two statements.
TYPE’S ;
> There are three types in control statement.
> CONDITIONS STATEMENT
> LOOPING STATEMENT
> JUMPING STATEMENT
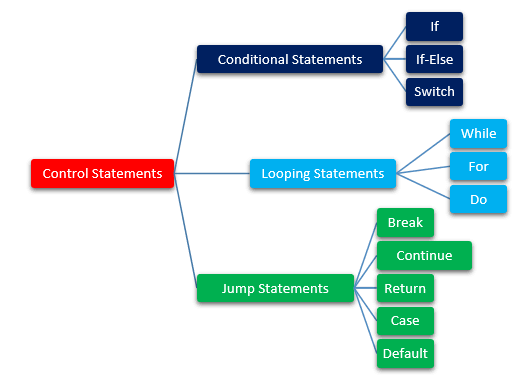
CONDITIONS STATEMENT ;
> this is fully controlled by condition.
> After that, the given condition is true. Another one true bolck statement will be execute.
> otherwise false block statement will be executed.
TYPES ;
> IF
> IF ELSE
> ELSE IF LADDER
> NESTED IF
IF ;
> It will go inside the block only if the condition is true otherwise, it will not execute the block.
SYNTAX ;
if(condition){
// statements (if Block)
}
//other statements
IF ELSE ;
> If the condition is true then, it will execute the If block. Otherwise, it will execute the Else block.
SYNTAX ;
if(condition){
// statements (if Block)
}
else{
// statements (Else block)
}
//other statements
ELSE IF LADDER ;
> the condition is true, then it will execute the If block.
> Otherwise, it will execute the Else-If block. Again, if the condition is not met, then it will move to the else block.
SYNTAX ;
if(condition){
// statements (if Block)
}
else if{
// statements (Else-If block)
}
else{
//statements(Else Block)
}//other statements
NESTED STATEMENT ;
> Nested if statement is if inside an if block.
> It is same as normal if…else statement but they are written inside another if…else statement.
SYNTAX ;
if (condition1) {
Statemen 1; //executed when condition1 is true
if (condition2) {
Statement 2; //executed when condition2 is true
}
else {
Statement 3; //executed when condition2 is false
}
}
SWITCH STATEMENT ;
>Switch statement allows program to select one action among multiple actions during the program execution.
SYNTAX ;
Switch(variable/value/expression){
Case : 1
// statements [];
Case : 2
// statements [];
default:
// statements [];
}